
Exploring the 5G NR (New Radio) Technology
Welcome to the world of 5G NR, the cutting-edge technology that’s revolutionizing how we connect wirelessly.
Imagine a world where everything around you is seamlessly connected at lightning-wavefast speeds with minimal delay. That’s the promise of 5G NR.
But first, let’s understand the basics. 5G NR stands for 5G New Radio, and it’s the latest standard in wireless technology.
It’s like the next big upgrade after 4G. While 4G is already pretty fast, it has its limitations when it comes to handling lots of devices or providing super high speeds.
Here’s where 5G NR is designed to be much faster, more efficient, and able to support a lot more devices at once.
It does this by using mmWave, which basically means it can transmit signals at really high frequencies.
This allows for super-fast download speeds, potentially reaching up to a mind-boggling 10 gigabits per second!
So, what does all this mean for you? Well, imagine streaming your favourite movies or playing online games without any lag or buffering.
Picture smart cities where everything from traffic lights to appliances is interconnected, making life easier and more convenient.
That’s the power of 5G NR mmWave it’s not just about faster internet on your phone, but a whole new way of living and interacting with the world around us.
This is getting interesting, right? So, in this blog, we are going to explore everything you need to know from is what 5G NR to how it differs from other technology types.
What is 5G NR?
 5G NR, or 5G New Radio, is the latest wireless standard that forms the backbone of the fifth generation of mobile networks.
5G NR, or 5G New Radio, is the latest wireless standard that forms the backbone of the fifth generation of mobile networks.
It represents a significant step forward in mobile broadband technology, aiming to fulfil the requirements outlined by IMT-2020.
IMT-2020, or International Mobile Telecommunications 2020, is a program that began in 2012 to develop 5G technologies.
One of the primary objectives of 5G NR is to bridge the gap between wireless and wired broadband by delivering performance comparable to fibre optic connections but at a much lower cost per data unit.
This means that users can expect faster and more reliable internet speeds, similar to what they would experience with a fibre optic connection, but without the need for physical cables.
Moreover, now let’s understand the key reasons for the development of 5G NR.
Why 5G NR is Developed?
5G New Radio (NR) is developed for several key reasons:
- To handle different frequencies well: 5G NR optimally support a wider range of frequencies < 6 GHz and mmWave bands up to 100 GHz
- LTE and HSPA aren’t great with super high frequencies: Unlike 5G NR, LTE and HSPA were not designed to be optimized for mmWave frequency bands.
- It can handle wider channels: 5G NR can support wider channel bandwidth up to 1 GHz resulting in fast speed and better use of airwaves.
- New ways to set up networks: 5G NR support new channel model profiles making them more adaptable to different places and situations. This helps improve how well our networks perform overall.
Frequency Range of 5G NR
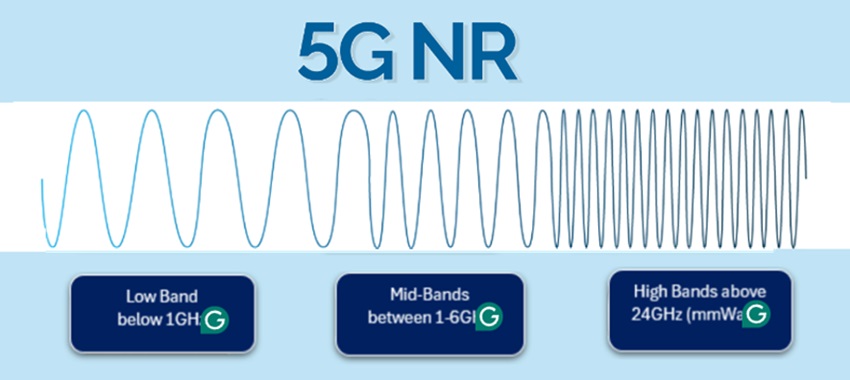
The frequency range of 5G NR is defined by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) which sets the standards for mobile telecommunications.
Moreover, 5G NR uses electromagnetic radio waves to enable communication. It uses three sections of bandwidth which are as follows:
- Low band (below 1GHz)
- Mid band (1- 6GHz)
- High band (above 24GHz)
The high band is also named as mmWave band or millimetre wave band. It uses two frequency ranges mmWave 5G FR1 and FR2.
Frequency Range 1
Frequency channel Bandwidth:
- The maximum bandwidth supported in FR1 (Frequency range 1) is 100 MHz.
- The available channel bandwidth options are: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, and 100 MHz.
Unlike LTE which supports 1.4 as well as 3MHz channel bandwidths the minimum channel bandwidth for 5G starts from 5 MHz.
Frequency Range 2
Frequency channel Bandwidth:
- FR2 supports larger bandwidths compared to FR1.
- Channel bandwidth options: 50, 100, 200, and 400 MHz.
- Additionally, FR2 allows for 800 MHz with 2400 MHz carrier aggregation (CA).
Moreover, if an operator is allocated 800 MHz bandwidth, they can’t use the entire 800 MHz as channel bandwidth.
Instead, they must split this bandwidth into two carrier elements and use it as carrier aggregation, with each carrier component having a bandwidth of 400 MHz.
Difference Between FR1 and FR2
For a better and clearer understanding, let’s examine the differences between FR1 and FR2.
| S.No | FR1 | FR2 |
| 1. | FR1 stand for Frequency Range 1 | FR2 stand for Frequency Range 2 |
| 2. | FR1 is the range of sub-Wave6 GHz frequencies | FR2 is the range of millimetre wave (mmWave) frequencies |
| 3. | Suitable for continuous coverage, high mobility and reliability | Suitable for applications that need high throughput, throughput such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and high mmWave definition video streaming |
| 4. | Support subcarrier spacing 15, 30 and 60KHz.
15 and 30 Khz are most commonly used. |
Support subcarrier spacing 120, 240 and 960KHz.
120 kHz is the most commonly used. |
| 5. | Support FDD, TDD, SDL and SUL Duplex mode | Support only TDD Duplex Mode |
Different types of Duplexing modes used in 5G NR
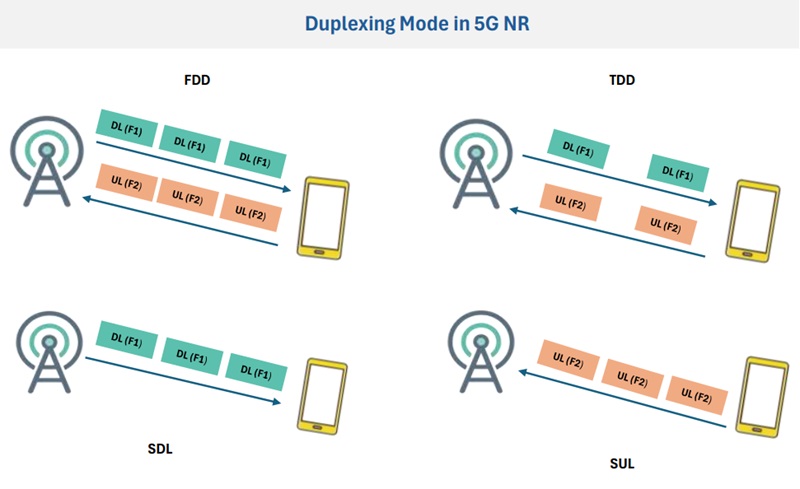
Here we can see we have a base station and we have a mobile device we say this as an UE (User Equipment).
Likewise, the signal transmitted from the base station towards the UE is known as downlink and the signals which are transmitted from UE to the base station are known as Uplink.
1. Frequency Division Duplexing (FDD):
FDD means frequency division duplexing, so in FDD what we see in the above picture there are some downlink transmissions and uplink transmissions.
The downlink transmission is noted by DL and they are happening on the F1 frequency.
In the uplink transmission which happens in F2 frequency, It means in FDD duplex mode we will be getting 2 frequencies which can be used for downlink and uplink simultaneously.
2. Time Division Duplexing (TDD):
TDD means time division duplexing which means we will be using the frequency F1 at different times.
We have only one frequency that is shared between uplink and downlink at different times.
3. Additional Modes
SDL is a Supplement downlink so in SDL there is one frequency that will be used for the downlink, so basically the SDL is used to increase the downlink capacity.
SUL is Supplement uplink where the frequency is used for uplink transmission.
Difference Between Different Network Generations: 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G NR
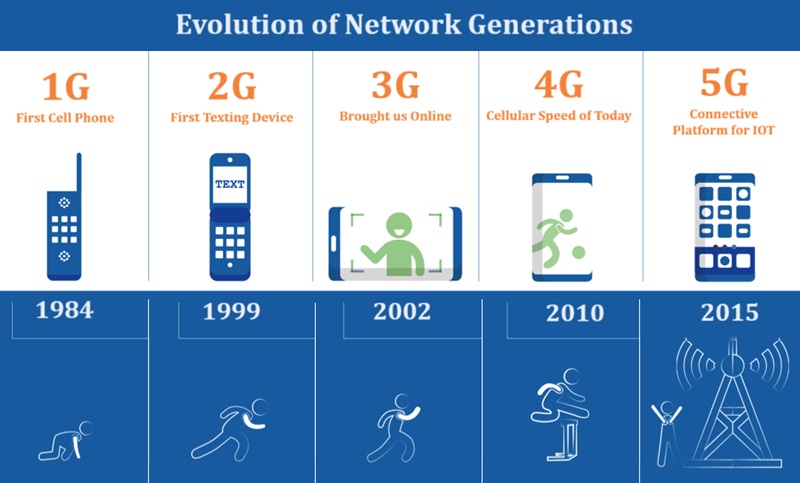
Throughout the years, mobile networks have evolved significantly, each generation bringing new technologies and capabilities.
We’ve come a long way from the first generation (1G) of mobile networks, which introduced basic voice calling, to the latest fifth generation (5G), which promises blazing-fast speeds and exciting new applications.
So to know more about different generations of technology, let’s take a closer look at the key differences between these generations.
|
Generation |
Developed | Technology Standard | Applications |
Speed |
|
1G |
1984 | AMPS | Voice Call |
2.4 Kbps |
|
2G |
1999 |
GSM |
Voice Call, Short Message | 64 Kbps |
|
3G |
2002 |
UMTS, WCDMA |
Video Conferencing, Mobile TV, GPS | 2 Mbps |
|
4G |
2010 |
LTE |
High-speed Internet, Mobile TV, Wearable Devices | 100 Mbps |
|
5G |
2015 | NR |
High-speed Internet, High-resolution Video Streaming, Remote Control Vehicles, Medical Procedures |
10 Gbps |
Summary
In summary, 5G NR (New Radio) is the latest wireless technology, paving the way for faster, more efficient, and interconnected communication.
It operates on various frequency bands, including mmWave, enabling speeds up to 10 gigabits per second.
Developed to bridge the gap between wired and wireless broadband, 5G NR promises to revolutionize how we connect and interact with the world.
Compared to previous generations like 4G, 5G NR offers significantly higher speeds and better support for multiple devices simultaneously.
So, with its advanced capabilities and broader frequency range, 5G NR opens doors to innovations like smart cities, seamless streaming, and immersive experiences.
Follow us and Stay Updated!
If you are lagging behind with the latest compliance news, updates, amendments and so on then we have various options for you to stay up-to-date.
Subscribe to our Free Monthly Newsletter, and WhatsApp Channel or watch our Publication Space to stay ahead with the latest regulations and notifications without spending a dime!