STARLINK (Connect the Unconnected)
It’s the space race, but unlike the 50s this race’s goal is to connect the world-including rural areas—to the internet. Elon Musk’s Star link satellite internet project aims to bring affordable, fast internet to underserved parts of the world. What is STARLINK: STARLINK is a Satellite Internet Constellation being constructed by SpaceX to provide
It’s the space race, but unlike the 50s this race’s goal is to connect the world-including rural areas—to the internet. Elon Musk’s Star link satellite internet project aims to bring affordable, fast internet to underserved parts of the world.
What is STARLINK:
STARLINK is a Satellite Internet Constellation being constructed by SpaceX to provide satellite internet access. The constellation will consist of thousands of mass-produced small satellites in Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which can communicate with designated ground transceivers.
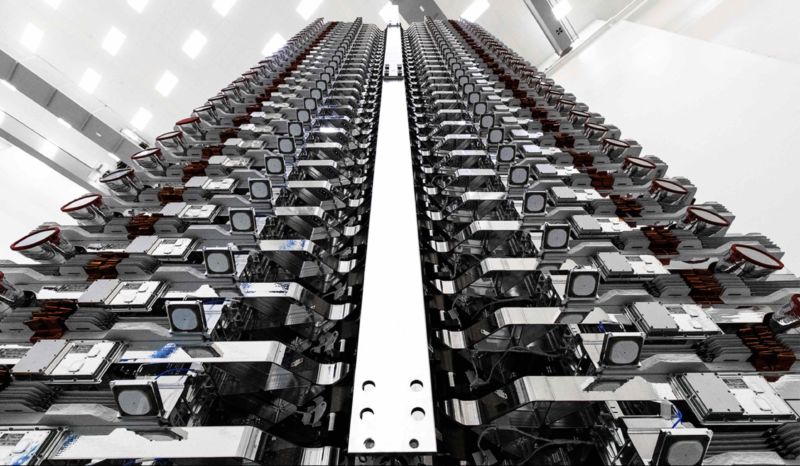

60 Starlink satellites stacked for launch at SpaceX Facility in Cape Canaveral, Florida.
image source: https://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2020/10/spacex-has-launched-enough-satellites-for-starlinks-upcoming-public-beta/
Journey of Starlink:
The development of the constellation network began in 2015, with the first prototype satellites launched into orbit in 2018. In November 2016, SpaceX filed an application with the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for a “non-geostationary orbit (NGSO) satellite system in the Fixed-Satellite Service using the Ku (12-18 GHz) and Ka (27-40 GHz) frequency bands. Since then, SpaceX has been updating, modifying and clearing all the regulatory requirement with FCC and ITU (International Telecommunication Unit). They started with a mission of deploying 42000 satellite in the near-earth orbit. Finally in January, after about three years’ worth of successful launches, the project surpassed to deliver 1,000 satellites into orbit
How Starlink works:
To be a part of Starlink community, one must connect to the constellation. The set up consist of a WiFi Router, Power Supply, Cables and Mounting Tripod. This has to be aligned to the Antenna which will connect to the nearest Star link satellite in the constellation. The constellation of satellite processes the data with each other through a laser beam and takes the data from the earth-based ground station. For now the top speed is around 150 Mbps with latency of 20-40 ms, which will improve with increase in number of satellites. In the future, Starlink has a plan of launching total 12000 satellite by the end of 2024.
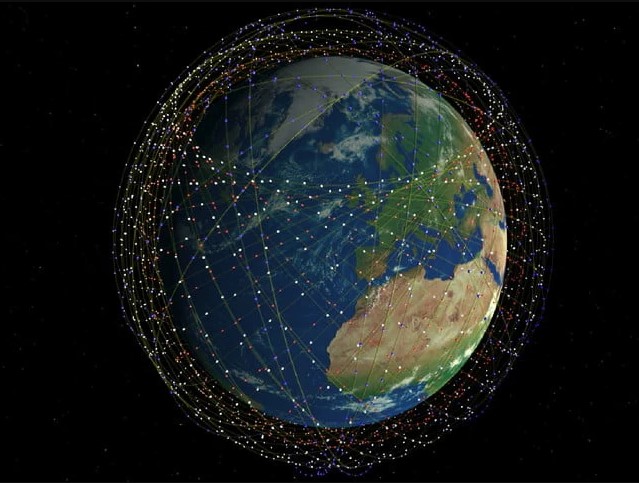
Image source: https://www.lmiadvisors.com/from-ligado-5g-to-orbital-debris-the-fccs-role-in-space-policy/
Problem with the fibre optics and how Starlink is solving it:
Fibre optics or ground-laid fibre-optic cable, which we all use for internet connectivity is still the fastest means of communication. But when it comes to providing the service to a rural user, one must deploy a cable connection from the nearest service provider centre. This is a very tedious, time taking and slow method to connect with the whole world. Further all the telecom giant looks for profitability, so if the net user base is not giving them profit, they will not provide the service to that location, as to save that cost.
Though Satellite constellation has its own disadvantages, but in the long run, we expect that it might take over fibre optics in the race to connect the globe. SpaceX agreement with Google Cloud Platform and Microsoft Azure to provide on-ground computer and networking services for Starlink, backs this fact that tech giants are welcoming this idea.
The brightness issue (Light pollution):
Astronomers claim that the number of visible satellites will overwhelm the visible stars and their brightness in both optical and radio wavelengths will severely impact scientific observations. As the Starlink satellites can randomly change their orbits, it wouldn’t be practical to schedule observations to avoid their effect. The International Astronomical Union (IAU), National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO), and Square Kilometre Array Organization (SKAO) have released official statements expressing concern on the same.
On 17 April 2020, SpaceX wrote in a Federal Communications Commission (FCC) filing that it would test new methods of mitigating light pollution, and also provide access to satellite tracking data for astronomers to “better coordinate their observations with our satellites”
Can Indians use Starlink beta program?
In order to offer satellite services over any nation state, ITU regulations and long-standing international treaties require the landing rights to be granted by each country jurisdiction. As a result, even though the SpaceX Starlink network has near global reach, broadband services to rural and underserved areas can only be provided in a few countries to date.
According to the Statistical study, India has approximately 700 million internet subscribers in 2020 and is on track to achieve 974 million users by 2025. In addition, by 2022, our rural population is estimated to reach approximately 506 million, and cable connectivity may not always be available. As a result, satellite technology seems to be the only option to connect the remote areas with internet.
In response to Starlink, the BIF, which represents companies such as Qualcomm, Amazon, Google, Microsoft, Intel, Nokia, AT&T, and Facebook, as well as a few government agencies such as C-DOT, BSNL, and India’s top technology institutes IIT Madras, Roorkee, and Hyderabad, stated that Starlink does not have ground or earth stations in India, nor does it have satellite frequency authorization from the Indian Space Research Organization. The BIF requested the intervention of the TRAI and ISRO in the matter.
View of the DOT:
Department of telecommunication has indicated that they have no issues with Starlink if they follow the rule of the land. Therefore, satellite internet service provider will require authorisation or license which comes within the unified license which can be ISP license or/and VSAT license. Here the, ISP license is required for providing internet services and VSAT is for clearing satellite regulations. It is expected that Starlink might provide its services in India by mid-2022.
Other players in the market:
- Amazon’s Kuiper Systems hasn’t deployed any satellite yet, but the company said it plans to launch more than 3,200 satellites.
- Sunil Mittal’s Bharti Group’s OneWeb is also on the same path. In the month of April 2021, OneWeb a satellite communications company backed by the Bharti Group, had launched 36 satellites. These satellites will provide high speed internet service. Going forward, OneWeb intends to launch global services by 2022.
- It is expected that China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation will be launching a smaller number of satellites to provide high-speed internet on earth.
Can I afford Starlink?
Currently the pre order costs around 99 dollars. The initial set up is 499 dollars, and the monthly subscription is 99 dollars. For now, prices are skyrocketing, so it is not affordable with respect to the middle class Indian customer, also the competition in Indian market is very high. In urban areas service providers like Jio, Airtel, VI are providing 1gbps broadband connection near the same price.
It is expected that the Starlink’s price may increase in India. Because, the bandwidth fee in India is very high compared to other countries. But with time and more advancement in technology and more player in the market, the cost will come down in future.
Conclusion:
Starlink will likely change the arena of internet distribution forever. In the year 2020, nearly 40% of the world still does not have a stable access to the internet. Starlink will add this non-connected mass as a new surge in the Internet traffic which will affect economies in various ways. New business opportunities will arise and it will positively affect all the sectors such as education, B2B, Logistics, Defence and Disaster management.