
LoRa Technology: Revolutionizing IoT Connectivity
LoRa technology has become a popular name in the field of the Internet of Things (IoT) because of its infinite potential. IoT refers to a network of interconnected devices that enables communication between physical objects, connecting devices, sensors, and applications to streamline our lives. Among the various IoT connectivity options,
LoRa technology has become a popular name in the field of the Internet of Things (IoT) because of its infinite potential.
IoT refers to a network of interconnected devices that enables communication between physical objects, connecting devices, sensors, and applications to streamline our lives.
Among the various IoT connectivity options, LoRa technology is well known for its ability to provide long-range, low-power communication solutions.
Low energy consumption and wide coverage range are two significant reasons why LoRa has become so popular in recent years.
But do you know what is LoRa and LoRaWAN Technology? If not, then this is the right article for you.
We are going to cover everything regarding LoRa and LoRaWAN technology to give you a clear understanding.
What is LoRa Technology?
LoRa, short for “Long Range,” is a Radio Frequency modulation technology for low-power, wide area networks (LPWANs), derived from existing Chirp Spread Spectrum (CSS) technology.
It operates in a fixed-bandwidth channel of 125 kHz for uplink channels (End Nodes to Gateway) and 500 kHz for downlink channels (Gateway to End Node).
It was introduced by Semtech in 2012. Unlicensed Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) bands are used for LoRa technology.
In India LORA technology primarily operates in the 865-868 MHz Frequency band.
What is LoRaWAN?
LoRaWAN is a low-power, wide-area networking protocol built on top of the LoRa radio modulation technique.
It manages communication between end nodes and network gateways as well as wirelessly connecting devices to the internet.
It allows for bi-directional communication between IoT devices and the network, meaning devices can both send data to the network (uplink) and receive data from the network (downlink).
Major Difference Between LoRa and LoRaWAN
LoRa is the physical layer technology that provides long-range wireless communication capability, while LoRa WAN is the network protocol and infrastructure that enables the connection of LoRa-enabled devices to the internet or other networks.
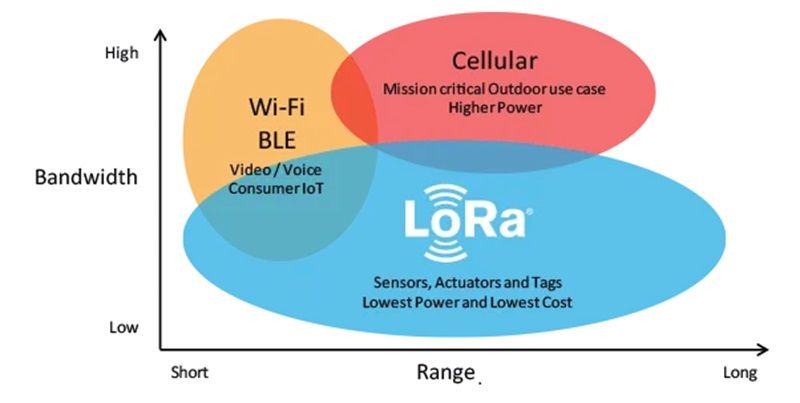
In the above diagram, there is a relation between Bandwidth and Range which shows that LoRaWAN is suitable for transmitting small-size payloads (like sensor data) over long distances.
Compared to competing wireless data transmission technologies, LoRa modulation offers a significantly greater communication range at low bandwidths.
Comparison Between LoRa and other Wireless Communication Technologies
|
Wireless Technology |
LORA | Wi-Fi | Bluetooth |
Cellular |
| Range | Long Range,
2-5 km (urban area) 5-15 Km (rural area) >15Km (direct line of sight) |
Short to moderate range, typically within a few hundred meters | Short range, typically up to 30-45 meters (Bluetooth Low Energy). | Varies widely, from a few kilometres to tens of kilometres. |
| Power | Extremely power-efficient, suitable for battery-operated devices. | Relatively higher power consumption is not ideal for battery-operated devices. | Low power consumption, suitable for battery-operated devices. | Low power consumption, suitable for battery-powered devices. |
| Bandwidth | Low to moderate, suitable for small periodic data transmissions. | High bandwidth, suitable for high-data-rate applications like internet access and video streaming. | Moderate bandwidth, suitable for wireless audio and peripheral connections. | High bandwidth, suitable for various applications including voice, data, and video. |
| Application | Ideal for long-range, low-power IoT applications like smart agriculture and environmental monitoring. | Commonly used for local area networking and high-speed internet access. | Used for connecting devices like headphones, wearables, and IoT sensors. | Ideal for mobile communication, including smartphones, data access, and IoT applications in areas with cellular coverage. |
The Architecture of LoRa Technology
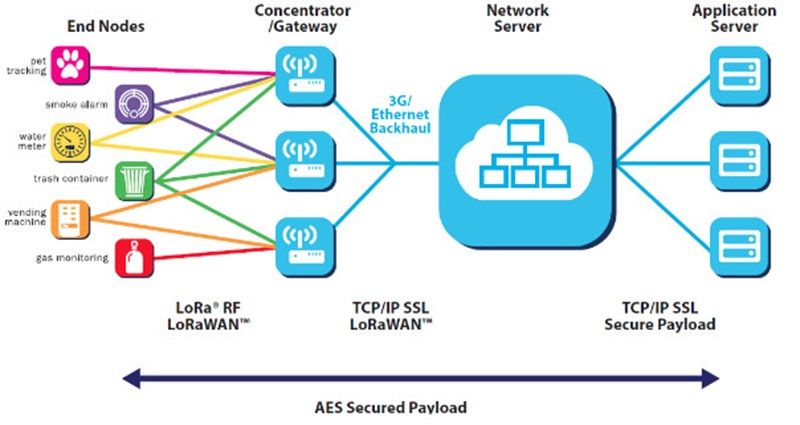
LoRa architecture is developed in a star topology.
The communication between the end node and gateway is bidirectional which means the end node can send data to the Gateway and can also receive data from the gateway.
Component used in LoRa Architecture
1. End Device: These are the sensors, devices, or objects that need to transmit data over long distances. They are typically battery-powered and equipped with LoRa transceivers.
2. Gateway: The Gateway operates on the physical layer and once the end device sends the modulated data packets viva LORA technology.
3. Network Server: The network server manages communication between the gateways and the application server.
It is responsible for routing data from multiple gateways to the appropriate application server.
4. Application Server: The application server is responsible for processing the data received from the network server.
It may perform data analysis, storage, and integration with other systems or applications
Benefits of LoRa Technology
1. Long Range: LoRa technology is capable of transmitting data over 15 kilometres in rural areas and 5 KM in urban environments, making it ideal for applications that require long-range connectivity.
2. Low Power Consumption: LoRa devices are energy-efficient, enabling battery-powered IoT sensors and devices to operate for years without frequent battery replacement.
3. Scalability: LoRa networks can accommodate a large number of devices, making them suitable for both small-scale deployments and large-scale IoT solutions.
4. Cost-Effective: LoRa technology is cost-effective because it operates in unlicensed bands, eliminating the need for costly spectrum licenses.
Does LoRa Technology require WPC Certification?

To facilitate the import of wireless devices like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zig-Bee, LoRaWAN, RFID etc. into India, Equipment Type Approval (ETA) must be obtained from the WPC department.
How Vincular can Help you?
Vincular will assist you in meeting your WPC certificate requirements to import or produce wireless products in India. We support you from product evaluation to compliance with Indian regulatory requirements.